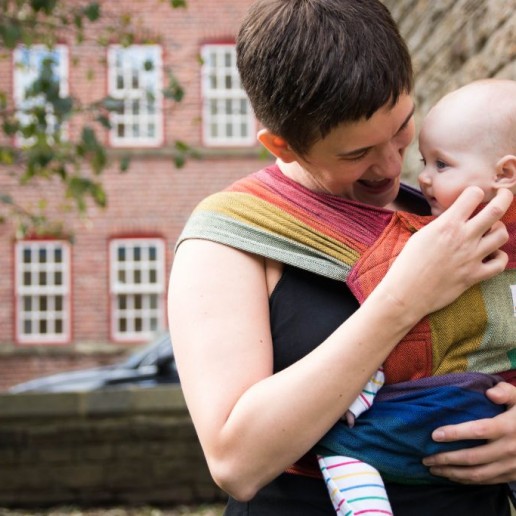
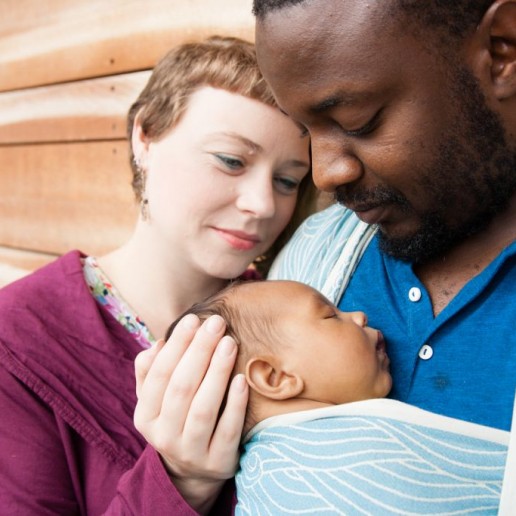
Secure Attachment and the "Fourth Trimester"
Secure attachment is the deep and enduring emotional bond that connects one person to another across time and space; a "lasting psychological connectedness between human beings" (Bowlby/Ainsworth).

Research shows that one of the strongest predictors for insecure attachments in children is to have a parent who lacks secure attachment themselves.
So, how do you build a secure attachment relationship with your child?
Secure attachment is created by loving responsiveness to your child's needs. It is not about your parenting style. Your baby may sleep in a crib or your bed, be fed from a breast or a bottle, be held in arms or a sling, be weaned in any style, be brought up by any combination of carer and still have secure attachments. It is not about subscribing to a particular parenting philosophy. You do not have to sacrifice everything - your identity, your sanity, your relationship, your job, your money or anything else at the "altar of childhood".
Building secure attachment is about having respect for a child's personhood, building their sense of self-worth within a consistent, loving and responsible relationship, regardless of their age or understanding.
Your child's humanity is as valuable as your own; neither more nor less. You are your child's advocate in the world and their greatest defender. You can provide for their every need, and they depend entirely on you and your surrounding network. They will learn whether or not they matter from how they are treated and how their requests for support are met. Securely attached children are confident that they will be cared for, and that any distress will be met by love. They are easily soothed by their caregiver when upset, are more able to be self-reliant, form positive relationships and generally have smoother paths through life.
However, their needs need to be balanced with that of the family, as a crumbling family dynamic will ultimately not be in anyone's best interests.
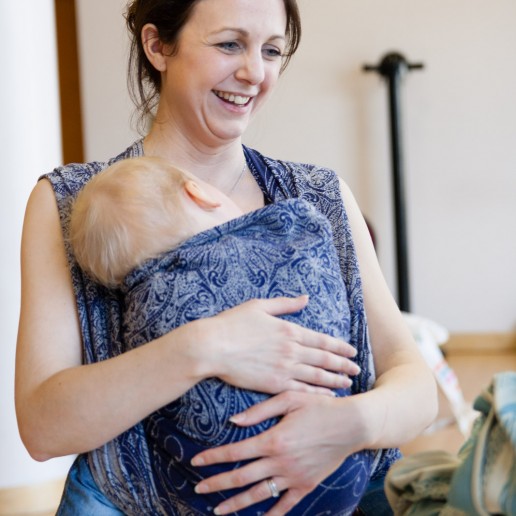
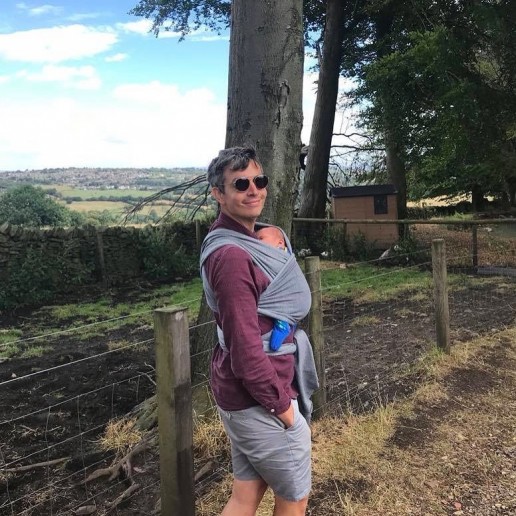
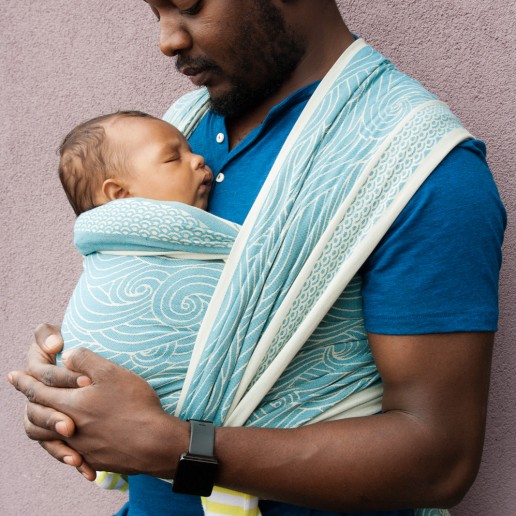
The "fourth trimester" is where attachments begin to form.
What is the Fourth Trimester?

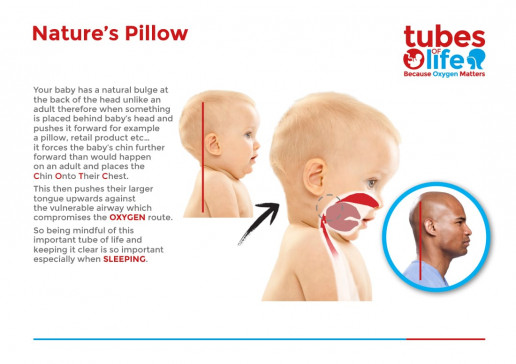
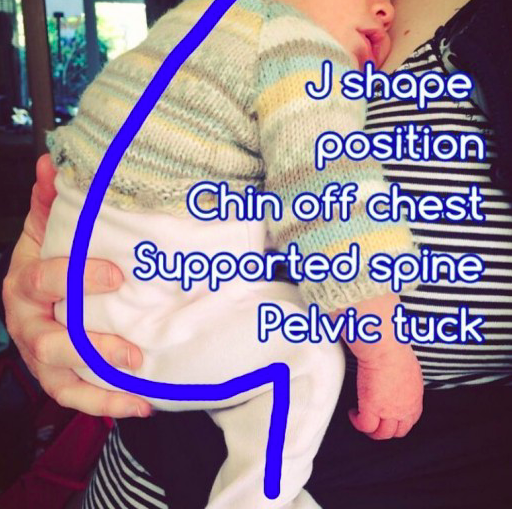
The ‘fourth trimester" is the period immediately after birth, a few more months of intense nurturing to allow a baby to continue with their essential development from a place of security and safety.
A baby who has spent all their life growing peacefully in the womb, gently compressed by uterine walls at the end of the third trimester, will find the sensation being born, followed by freedom and open space in the outside world enormously different. Limbs that have been limited are suddenly free to stretch wide, darkness has turned to light, the muffled gentle rhythmic sounds of the mother's body have been replaced by loud, unfamiliar noises or deep silence. Constant gentle motion has turned into complete stillness or sudden movements. No wonder that when babies are held close, rocked and soothed, contained in soft boundaries once more, that they settle; this feels right and familiar.
The "fourth trimester” is all about gentle transitioning from the peace and stability of the womb towards active involvement in a new world.
A newborn needs to be supported to gain skills and strength at a steady, individual pace from the security of an unshakeable foundation and place of comfort and familiarity. Being held, close to familiar noises and scents is essential to development and positive learning; the infant brain is growing rapidly and forming new connections all the time. Connections that are reinforced frequently will persist into later life, whereas those that are rarely used will wither away. It is worth taking the time to ensure that these unconsciously forming connections are positive ones. Young infants do not have the cognitive development to behave in "manipulative" ways; but they do learn to trust someone who proves reliable time and again as these pathways are reinforced. They will be startled and upset when this love is withdrawn.
The importance of responsiveness
If you are sensitive and responsive to your baby as they begin to communicate their needs with you (by crying, wriggling, yawning etc) they will learn that they matter to someone. If they are uncomfortable, the people they are learning to trust will soothe them. When they are hungry, they will be fed, when they are tired, they will feel secure enough to sink into sleep. They will not be frequently left alone unattended for long periods of time, and will not be left to exhaust themselves in calling for someone who never comes. When they cry, loving arms will be there to comfort and keep them safe. These same arms will show them the world and provide a safe place that facilitates learning. Carrying matters; babies need it. It does not make them clingy, rather, the solid foundation of secure attachment relationships will be the springboard to confident independence later in life.
How does babywearing help?
One tool that can help you meet your child's need for loving contact in these early months is a soft carrier that holds them in a comfortable, safe and anatomically respectful position. Such carriers will help you to meet their needs to be close to you while allowing you to be hands-free for daily life. There are many other positive reasons to carry a child; such as reduced crying, reduced plagiocephaly and more. Parents benefit too, for example carrying can be helpful for those with postnatal depression, and increase overall activity levels. This idea is not new; most of the world’s families across history and cultures have used some form of sling to make life work.
You can find out more from your local sling library or consultant; there are hundreds across the UK. They will help you to find the right type of carrier for your needs.
What about my older child?
Attachment relationships continue to form beyond the early months and children's brains are very "plastic". Warm, responsive, emotionally available parenting will help to build a child's sense of self-worth at any age. There is evidence that "mind-minded" parents (ie those who treat their children as intelligent, relational individuals with feelings, and speaking to them in such a way) seem to have children with more secure attachments. Active play and laughter, as well as consistent loving boundaries help to reinforce neural connections that the primary caregivers are a reliable source of security; forming strong foundations for the future. Read more about how carrying can help the learning brain.
References
Bowlby J. (1969). Attachment. Attachment and loss: Vol. 1. Loss. New York: Basic Books
Ainsworth, M. D. S. (1973). The development of infant-mother attachment. In B. Cardwell & H. Ricciuti (Eds.), Review of child development research (Vol. 3, pp. 1-94) Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ainsworth, M. D. S., Blehar, M. C., Waters, E., & Wall, S. (1978). Patterns of attachment: A psychological study of the strange situation. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Sutton Trust; Baby Bonds Parenting, attachment and a secure base for children. March 2014 Research by Sophie Moullin, Jane Waldfogel and Elizabeth Washbrook
http://www.parentingscience.com/attachment-parenting.html
Rethinking Maternal Sensitivity: Mothers’ Comments on Infants’ Mental Processes Predict Security of Attachment at 12 Months; J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Vol. 42, No. 5, pp. 637–648, 2001
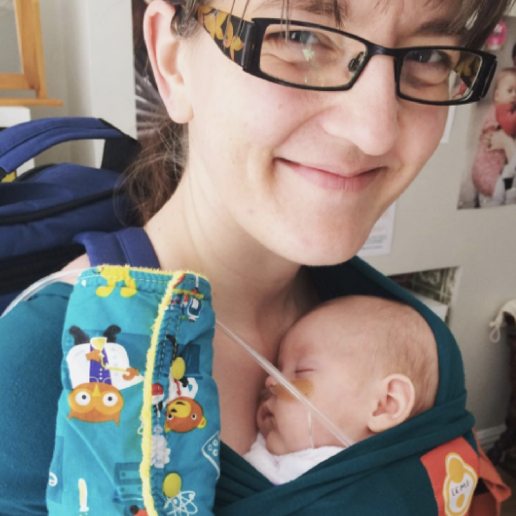
Carrying a Premature Baby, personal story
This is Kay and Alex's story of carrying a premature baby. She tells us about their lives together and what role slings have played in their rocky journey. It is a truly inspiring story of great courage and endurance and I am honoured to have played a small part.
"For as long as I can remember I have wanted to be a mum, but my real journey to parenthood started 5 years ago. I decided that I didn't want to wait for the "right person" to come along and started looking into fertility treatment for single women. Unfortunately the process wasn't was easy as I expected; after lots of tests and surgery I discovered that I had endometriosis which may affect fertility..
I started out doing IVI with donor sperm but after two attempts with no success it was suggested that IVF might have a better chance of working. I decided to take part in the egg-sharing programme to reduce the cost and hopefully help someone else too. During this time there was a lot of compulsory counselling to ensure I was aware of all potential outcomes. I'm very lucky that I have a fantastic support system of family and friends around me, especially my parents.
The first attempt at IVF was not straightforwards, I got 14 eggs, (7 of which were donated), but only one was fertilised. This was put back and I got a chemical pregnancy but miscarried. I also got a relatively rare condition called Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) which made me really ill and I had to be hospitalised on numerous occasions. Due to the poor fertilisation rate it was thought that I had poor egg quality so had to pay the full cost of IVF treatment (as a single woman I was not entitled to any NHS treatment.)
On the second IVF attempt, medications were reduced to try lessening the risk of OHSS but because doctors were anxious about this, the egg collection was done too early and 5 eggs were lost during retrieval. This attempt was unsuccessful. I again got OHSS but much milder this time. The emotional rollercoaster or IVF is unimaginable and the hormones of treatment don't help! You spend all your time so focused on preparing to become pregnant, trying to stay positive, eat well etc, then once the embryo is implanted you have the longest two weeks praying you are pregnant and counting down to the day you can take a pregnancy test... but as soon as it is test day comes you don't want to do the test because you are until then "Pregnant till Proven Otherwise" ( PUPO). Internet support groups become your sanctuary because others undergoing IVF can understand what you are feeling, while your family and friends sometimes don't understand why you put yourself through so much. IVF became my only focus.
After the second attempt I had an eight month break to save up as I had used all my savings. I decided that the next would be my last attempt and I would do everything I could to try to help it work so I would have no regrets. I changed my diet (cutting out all processed food), saw a nutritionist, had regular massage (including Mayan abdominal massage) and acupuncture. We changed the IVF regime to one that had a higher chance of success but also a higher risk of OHSS. It was a risk I was willing to take. I had partly given up hope of this round working, as I got two fertilised eggs out of 19 when I began getting the OHSS symptoms again on day 2.
I did a home pregnancy test two days before test day..... and it was positive!
I didn't know how to react, so burst into tears before laughing maniacally then calling my best friend and my parents. The excitement wore off quickly though when I was admitted to hospital with OHSS at just 4+1 weeks. At a point when I had hoped that the hard part was over, it turned out that this was just the beginning of another difficult journey.
I continued to have tightenings but tried to ignore them as everything else seemed OK. Then exactly two weeks later after my scan at 21+6, I started with the smallest amount of bleeding. Again I was reassured as baby seemed OK and it had settled, possibly caused by a cervical erosion, and just to observe. I continued spotting on and off but nothing major, until I was at work on a shift on labour ward at 23+1 weeks pregnant.
I had a significant bleed and was terrified. I felt it was too far on in the pregnancy to lose the baby now but it was far too early to be born. I burst into tears. I am so grateful that I was at work surrounded by fantastic colleagues. I was admitted to the antenatal ward for observation overnight and I didn't go home again.
I continued to have tightenings and bleeding to varying degrees over the next three weeks. Getting to 24 weeks was a major milestone and I was given steroids to mature the baby's lungs. At around 25 weeks my waters went though because of the bleeding it wasn't obvious. Baby was breech and because of the situation I kept being told I might be taken for a Caesarean if bleeding increased or I went into labour. I saw paediatricians who told me stark statistics about survival rates and disability. As a midwife I knew these things but as a mum it just didn't sink in. I was tearful and losing hope. At 25+5 I had a major bleed that got me taken to labour ward and starved in case it continued and and I needed theatre. I spent the next two days in high dependency being observed and in denial.
Writing it down now it seems so silly but even given the bleeding, tightenings and water break it still never clicked to anyone that the pain I was in could be labour. At exactly 26 weeks I was found to be 7cm dilated. Two hours later I had a vaginal breech delivery complicated by the head getting stuck.
Alexander Benjamin was born weighing 1lb 12 oz and in a very poor condition.
The room was full of people but no-one was saying a word. Looking back at his notes now it says it took 18minutes to stabilise him before taking him to intensive care but it didn't feel that long to me. It seems awful to think about it now but at that point once Alex was born all I felt was relief. I was glad the pregnancy was finally over after months of feeling ill and stressed. I had spent the last few weeks trying to detach from the pregnancy as I feared the worst, but in the moment when Alex was taken away and we (myself, my parents and my friend) were left alone the silence said it all.
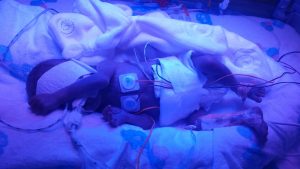
Only I was allowed to touch him but couldn't hold him yet.
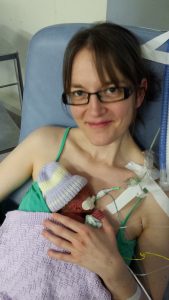
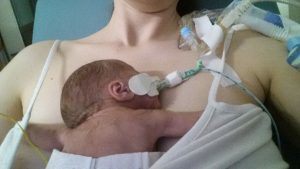
It felt complicated at first getting used to the technique of wrapping and because of all the monitoring it would often take someone else to help me get all the wires sorted, but once Alex was put into the sling he fell straight to sleep. I noticed that often his heart rate and oxygen sats would improve too and it made me even more determined to keep him close.
Our journey through special care gives me mixed emotions. On the one hand I would never wish this experience on anyone. The constant stress, not just for myself but also family and friends around me. The fear that if I leave, something might happen. Every time the phone rang panic would set in and don't even get me started on the paediatricians coming up to the ward!
However, my life has changed completely in so many good ways. I have realised and experienced how fantastic the care is from my colleagues. I have become closer to my family and friends and I love watching my parents with Alex. I feel I will be an even more sympathetic and understanding midwife and I hope my practice will change to support women who go through similar experiences. Most of all I have realised my dream of becoming a mum and to the most incredible little fighter I have ever met.
I feel I have a strong bond with Alex and many people have commented on how well I can read him. I believe it is because of staying close to him as much as I have and having him in the sling has facilitated this.
Alex has Chronic Lung Disease and came home on oxygen in March. He is doing incredibly well on the lowest level now, but transporting the oxygen has been a bit of a challenge for me. The canister is heavy and the container rucksack has narrow shoulders so has hurt my shoulders; trying to balance that weight against Alex has not been easy. At times I have felt isolated simply because of that. However I have met some wonderful people on my journey through special care and in the sling community (often the two groups mix!) and we wouldn't be where we are now without these challenges.
We are still using our Hana wrap, and I've been trying out a snuggly Sleepy Nico! I've learned how to use woven wraps; we are beginning to back carry; the end of the oxygen is in sight! Time to tuck Alex up into the Sleepy Nico and reconnect after a long day.
Positive Effects of Carrying for Society
The positive effects of carrying for society are many; making a change at an individual level can have a significant impact when lots of people do it! In-arms carrying and using slings is one way that we can change the future that we all have to live in.
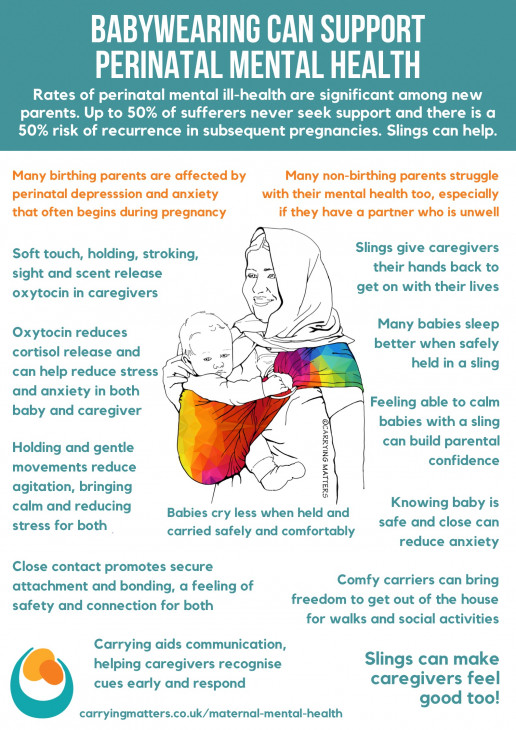
Possibly one of the most important positive outcomes for carrying for a parent and the society we live in is the effect it can have on mental health, which is a society-wide issue.
Western society is increasingly fractured and isolated, with a decreased sense of local community and shared care. The burden of mental unwellness in our society is growing, and becoming a parent with this background can be very tough indeed.
The birth of a baby is often an overwhelming time for both parents, especially when also faced with the expectations and demands of a fast-paced culture that often judges people by their apparent productivity and appearance. It is no wonder that postnatal depression is on the rise – affecting at least 10-15% of new mothers. This is likely an underestimate as parents feel ashamed to admit their feelings, with the effects of hiding their struggle having significant knock-ons for the whole family.
Fathers are often unrecognised to have the condition themselves, and this all adds to an increased risk of children coming to harm. This is a terrible indictment on our culture and its lack of care for some of the most vulnerable individuals in our communities.
The way we live now isn’t going to change overnight; funding for parental leave or greater support for mental health isn’t going to become suddenly available, and the media bombardment of products for parenting won’t vanish. But neither are the emotional needs of young children going to go away, especially if we want them to grow up well and be happy, confident mature individuals who are well integrated into society.
We need to find ways to nurture our children while still functioning as our culture expects us to, and this is where carrying children (often using a sling) can help. Carrying children encourages and protecting parent’s precious closeness with small children while helping to build the bonds that will be the foundations for a positive future. Giving children a secure and confident start in life pays dividends later for the whole of society.
- Families who enjoy secure attachments and strong bonds are more likely to weather the early years of parenting safely and build resilient children with a secure self-esteem. This will help to counteract the growing burden of mental "un-health" especially as funding for mental health services continues to decrease. Carrying (and using slings), via oxytocin release, helps to build these bonds; and can improve resilience to the Adverse Childhood Experiences that so many children experience. Read more about ACE's here.
- Anything that improves mental health and assists families struggling with PND is worth investing in, especially something as accessible and low cost as a carrier.
- A very sobering review of international attachment studies done by the Sutton Trust found that infants under three years who do not form strong bonds with a parent “are more likely to suffer from aggression, defiance and hyperactivity when they get older.” They found that up to 40% of children lack this secure bond with their parents, and this is likely to lead to their own children also suffering from insecure attachment; a vicious, repeating cycle. “Parents who are insecurely attached themselves, are living in poverty or with poor mental health find it hardest to provide sensitive parenting and bond with their babies.”
- They also found that children with weak attachment were more likely to be obese later in childhood (with subsequent effects on their long term adult health).
- Communities are the normal social structures of the human species; finding common ground and sharing the strains of life together keeps us going. Many families find community among like-minded parents; most sling users make strong supportive friendships within the sling community.
- Carrying keeps us active; movement is essential for health and fitness. Dynamic carrying in arms (if possible) helps children to hone their growing neuromotor skills, and carrying young children (or those with tired legs) is good for adults too; bone remodelling, muscle health and posture.
- As the rates of breastfeeding are higher in carried babies, the health benefits of breastfeeding will be more marked in societies who carry a lot (reduced breast cancer risk, reduced osteoporosis, increased transfer of antibodies, to name just some.)
- Babies who are carried are more content and cry less. Crying is very stressful; and successful calming of a distressed baby will build a parent’s confidence in their ability to care for their child and also reduce the feelings of tension in social gatherings or in large public open spaces.
- Carried babies may have had less ear infections, less corrective treatment for plagiocephaly, and thus have been less in need of the NHS budget.
I believe that health care professionals should therefore promote frequent carrying of infants to achieve the best possible outcomes for families, and for the long term benefit of the societies they live in. It is a low cost intervention that can have far-reaching effects.
Positive Effects of Carrying for Parents and Carers
In-arms carrying and using slings doesn’t just bring good things to babies – they can make a real difference to parents and other caregivers too. Read more about the benefits of babywearing for adults here.
- It encourages bonding and deepening of a loving relationship via the release of the hormone oxytocin; having baby close heightens the parent’s awareness and can increase their responsiveness to their baby’s needs. You can read more about the effects of oxytocin here.
- It can increase parental confidence. The parent may be more “in tune” with their baby, as the carried child is part of the parent’s personal space, and the parent will be more aware of changes in a child’s mood, and thus be more able to respond to the child’s facial expressions, gestures and vocalised needs sooner. This will build mutual trust and contentment.
- There is evidence to suggest that sling use can help with perinatal mood disorders such as postnatal depression, in part due to oxytocin release and in part due to increased bonding.
- Fathers and other care-givers will be able to use a sling as well, increasing family connections and helping baby recognise more people by their voices and scent. Sling use can be very valuable in giving family members “cuddle time” and can be an useful tool for childminders as well.
- Slings can provide “hands-free” parenting, which can be very useful, such as making a quick snack, interacting with an older child, doing the housework or other chores. A “fussy” baby may calm and settle in a sling, allowing the parent more choice about how to use their time.
- Slings can provide opportunities for physical exercise and mental stimulation; a new skill to learn and a new social circle (social sling meets, for example!) Many people find that carrying their children on walks helps to lose weight and tone muscles. Dynamic (in arms carrying) is also a good workout!
- Slings can provide greater access to the world – in a good sling the only limitations are where your feet can take you. Onto the beach, off the beaten path, up a tower, onto crowded public transport, around busy airports, the world is your oyster!
- Slings can provide comfort and nurturing for older children as well.
Positive Effects of Carrying for Baby
Carrying your baby is essential to their normal physical, psychological and neurological development. Human bodies are adapted to be a carrying species, it is part of our evolutionary history, however, our bodies are not as fit or as strong as our nomadic ancestors. It can be hard to carry in arms for prolonged periods of time. Nevertheless, babies need to be held, so a good, safe sling can be very useful in to help with increasing carrying frequency.
Remember, it is the relationship of closeness and loving touch that matters, as well as the position adopted in a good sling. The type of sling or the fabric that you use is just personal preference.
The benefits of babywearing- or the positive effects of carrying for baby are many; here are a few.
The positive effects of babywearing for baby are many; here are a few.
- It encourages bonding with the parent and helps to meets baby’s strong need for a sense of security and attachment, which will lead to greater confidence and independence later in life, as well as greater resilience and better long-term physical health.
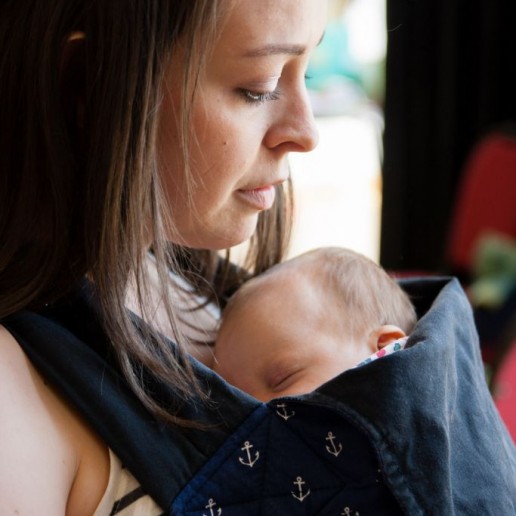
- It helps to regulate temperature, heart and respiratory rates, and emotional and physical growth. This can be especially useful for premature babies (the term “kangaroo care” and “fourth trimester” come from this concept) or children who are unwell.
- It promotes and encourages the establishment of a successful breastfeeding relationship, in part due to the oxytocin release from the soft touch. Mothers who carry their children in soft slings are more likely to breastfeed beyond the early weeks.
- Soft touch has many benefits for neurodevelopment and and helping the social brain to form.
- Regular close skin contact is believed to help babies regulate their circadian rhythms better and distinguish the difference between night and day sleep.
It reduces crying, both frequency and duration, (Hunziker and Barr 1986) and can improve sleep. It is safe for your baby to sleep in the sling, if the airway is well protected. Less crying means more time to be in “quiet absorption’, promoting learning and positive interactions with the world. The Esposito study discusses some of the mechanisms behind movement and how carrying is calming for babies.
- Babies with colic can be hard to soothe, but the motion gained from being gently rocked in a sling while the parent/carer walks may help to settle them, and also the parent/carer may feel less helpless. There is no evidence to suggest that babywearing actually reduces colic itself.
- Many parents of reflux babies spend a lot of time holding them upright and have tired arms and sore backs! A good sling that supports an upright position can thus reduce regurgitation and the discomfort of reflux. A spread squat position helps relax puborectalis muscle, to aid bowel elimination.
- The motion experienced by a baby being held by the carer allows the vestibular balance apparatus to develop more rapidly and enhances neuromotor development and muscle strength. It improves neck and head control, but is not a true substitute for “tummy-time” (tummy-time head-lifting is against gravity from a prone position). This is more marked with dynamic in-arms carrying (where this is possible). A sling or carrier should never be used as a prolonged restraint (unless danger is present such as crossing the road).
- Children should always be encouraged to be active as much as possible (WHO 2019) and if they want to get down and it is safe and practical to do so, this is ideal. However, this doesn’t mean that a child who is otherwise very active needs to be automatically removed from the sling after a certain amount of time. Sleeping babies do not need to be disturbed, just gently adjusted to ensure safety.
- It is believed to encourage sociability and language development; being able to hear the parent’s voice close up and watch their interactions with the world and other people from a higher vantage point is beneficial and also aids formation of family relationships. Studies into reduced talking in outward facing buggies highlights the importance of children being able to communicate easily with their carers.
- It allows baby to retreat from an overwhelming world and snuggle into the parent’s body for respite when needed. This is harder to do with world-facing carries, so encouraging parental responsiveness with front-facing out positions is important. (The challenges of facing forwards is covered in more depth here)
- Babies can learn very easily from a place of consistent safety, as their brains are not engaged with mere survival.
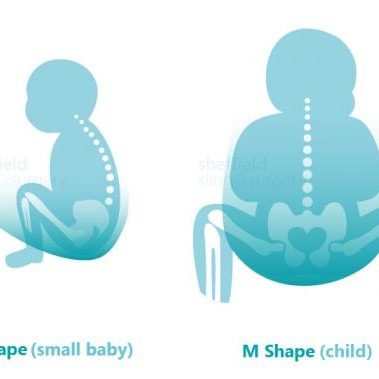
- Good, correctly designed slings that encourage the physiological spread-squat "M shape" position (that mimics hip-perching) can help prevent hip problems later in life in those children at risk of hip dysplasia. There is currently no convincing evidence that narrower based carriers cause hip dysplasia in otherwise healthy hips.
- Babies who are carried are less at risk of plagiocephaly (the flattening of the skull bones at the back of the head from prolonged periods lying on the back, more common since the “Back to Sleep” campaign). Slings are recommended as one solution (by the NHS, too!)
Further reading
"Why Babywearing Matters", Rosie Knowles, 2016
To have and to hold: Effects of physical contact on infants and their caregivers, Infant Behavior and Development, Volume 61, November 2020
Read some more articles about why carrying and using slings are good for babies below
Attachment, Babies and Carrying (HuffPost)
Secure Attachment and the Fourth Trimester
Adverse Childhood Events and building resilience in children
Seven Reasons to Carry your Baby (HuffPost)
Why Carrying Matters (Juno Magazine)
If you would like to read in more depth on this subject, my book “Why Babywearing Matters” discusses much of the evidence base for the importance of carrying. It is normal behaviour for the human species to carry their infants close to their bodies; the book considers the anthropological, physiological and psychological reasons for this. Carrying really matters.
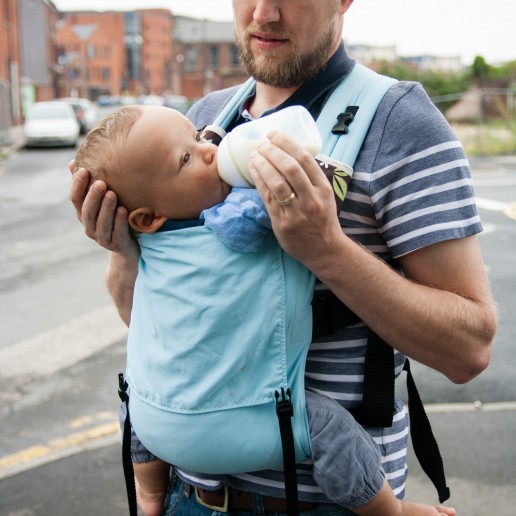
Breast and Bottle Feeding Safely in a Sling
Carrying babies is a wonderful way to encourage successful and more long-lasting breastfeeding, as the frequent skin to skin contact and the building of loving relationships help to stimulate oxytocin release.
Oxytocin release (which stimulates let-down) becomes conditioned to the mother’s experience and emotions; the touch, sight, smell or cry of her baby, as well as thoughts of her baby and the natural rhythm and expectation that baby will be hungry soon.
A sling that allows ease of access to the breast encourages responsive feeding, helping the harmonious nurturing relationship to flourish.
Mothers can go about their daily tasks or care for older children while their child’s need for nurture and nourishment can continue uninterrupted. This is normal human behaviour.
If the mother is in distress, unwell, or struggling with postnatal depression or anxiety, her feelings will inhibit oxytocin release and have an impact on breastfeeding. Close physical contact with her child as well as effective emotional support can help a feeding relationship to recover.
A comfortable baby carrier can thus be an excellent solution for a breastfeeding mother and baby who have had a complex start. This can be especially valuable after a difficult labour and birth or a prolonged separation for medical reasons.
The carrier can help create a safe space for the dyad, keeping them close together, allowing them to heal each other, encouraging the hormones of love and bonding to flow. This has a positive impact on breastfeeding.
If breastfeeding comes to an end, the baby carrier can preserve the growing relationship by keeping mother and baby in close contact and help it to continue to blossom.
There is always more of a risk to safety when combining breastfeeding with babywearing and it must be done well. Here’s my guide to safe breast and bottle feeding in a sling!
I meet a lot of pregnant ladies in the course of my varied roles, and many new mums, and one of the questions I am most frequently asked is “Will I be able to feed my baby in a sling?”
It’s an important question to deal with, as it crops up so regularly, and for some, is one of the criteria for choosing the right sling for their needs. The simplest answer is that, “Yes, many parents are able to feed their babies in slings, from the breast or from the bottle.”
But this then leads to other vital questions…
1. “Why might you want to be able to feed in a sling?”
2. “How can you keep your baby safe while feeding?”
3. “How can you make feeding in a sling as easy as possible?”
4. “What slings can be helpful for feeding?”



1) Why might you want to feed in a sling?
Most commonly, mums of more than one child find being able to feed the baby on the go very useful. This is especially so if they are feeding responsively, as recommended by the WHO, and have an older child who needs their parent just as much. Quite often, they will have had some experience of breast or bottle feeding already, and may be very familiar with their sling, and will be “old hands” at combining the two skills.
Mums of older children who can feed quickly in a sitting upright position may also find a sling an invaluable and very convenient tool for getting on with daily life.
For mums of small babies, it may be that the sling will be useful to carry their child to a place where they can be taken out to feed in peace and comfort. For others, being able to have baby partly supported with the sling and with one arm may allow a “third hand” to work on achieving latch, and can prove very useful for facilitating feeding. For others and once feeding is established, it can allow some simple multi-tasking rather than being pinned to the sofa.
On the whole, it may help to consider each element as a separate skill to master – how to feed, and how to use the sling, and learn how to combine them safely, however, for some, the sling can actually be an aid to achieving latch. Practice will, of course, be needed, like with every new accomplishment!
2) How can you keep your baby safe while feeding?
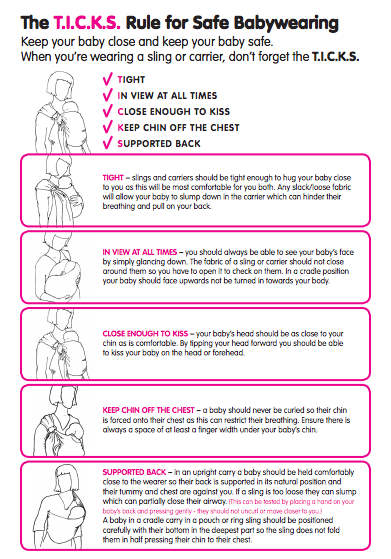
All the basic rules of sling safety apply when carrying a baby. The TICKS guidelines and the ABC reminders are below. However, there are different considerations needed with feeding in slings (as baby may not be close enough to kiss, for example). As always, protecting the airway and ensuring breathing is unobstructed is of paramount importance.
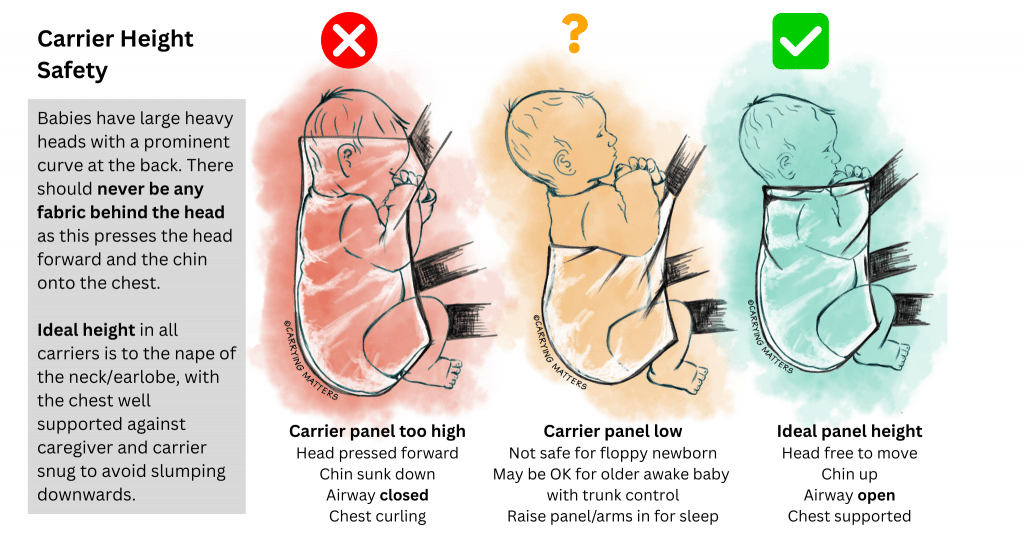
Babies are not mini-adults and are not able to breathe easily through their mouths for the first few months of their lives. They breathe mostly through their noses (allowing them to breathe while feeding), so unobstructed nasal airways are really important. This is why babies may struggle more than older children with mild respiratory infections affecting the small nasal passages, and explains why simple colds and respiratory viruses (eg RSV) can have serious impacts on newborns, as can any sinking of the chin onto the chest, closing the airway. Increased vigilance is needed during sleep, as muscle tone relaxes further. Feeding of any type in the carrier must be done with great caution as babies can slip into sleep as they finish their feed and airway can become obstructed. This is why we are always so careful to mention no fabric behind the head at any time, a fact often missed by carrier companies who focus on “head and neck support”.
Therefore, while a baby’s mouth is engaged with the process of sucking and swallowing, his only patent airway is his nose. It is important for the carer to be consciously aware of any potential obstruction, either external (from sling fabric, or breast tissue, or clothing ) or internal (neck bent over too far) and able to rectify it rapidly when required.
Whether feeding upright, or slightly reclined, the safest positions are…
-
those in which the parent is actively engaged and frequently checking on their child, and able to recognise any changes
-
those that ensure a good air supply at all times with no fabric over the head and chin off the chest (check you can fit two fingers underneath if you are unsure)
-
those in which baby’s head is aligned with their spine and only turned slightly to one side if needed
-
those in which baby’s back and occiput (lower part of the back of the head) are appropriately supported
-
those in which baby’s knees are above the bottom and hips are flexed (bent upwards)
-
those that ensure that a baby who has finished feeding or has fallen asleep is returned to the most optimal upright position to keep airway supported and open.
The choice of best position will vary from person to person, depending on the individual circumstances, however, the majority of successful “on-the-go” feeding is done in the upright position.
In my opinion, the greatest risk comes from breastfeeding in positions where baby is held face inwards towards the breast, with sling fabric pulled up over the back of the head, so the face is pressed firmly into breast tissue or the child is curled over into a ball.
Please note this dangerous position is not the same typical gentle reclining in-arms “cradle” positions where the head is well supported in the crook of the elbow and the chin is not on the chest. This is the most common breastfeeding position, with a sling adding a little support, almost like a cushion or a hammock, to take some of the weight off the supporting arm and give you one hand free.
What should a feeding carry look like?
Baby’s head should be completely free of fabric, being supported by the sling up to the nape of the neck, able to latch and delatch as needed. Their lower body should be well supported from knee to knee, either by wrap fabric well and snugly tucked up between your bodies, or a well tied/securely buckled waistband. Both of baby’s arms should be positioned around the feeding breast or bottle, just as if in arms, and the head should not be at an awkward angle. Feet should be free of fabric and baby should be comfortable and easily able to reach the nipple. If baby is able to achieve a good latch from this position, he/she should be able to feed if ready. Some practice may be needed for both of you!
Feeding in slings is more risky if you have a snuffly baby who is needing to delatch frequently for some mouth breathing, and finds herself unable to do so as her head is not free to pull backwards for a little extra air.
Babies should never be left to sleep in feeding positions as their disproportionally heavy heads can too easily droop or be folded over, with subsequent obstruction of their airways.
**Please remember that loosened slings with longer tails can present a trip hazard if you are feeding on the move.**
In general, it can help to think of the sling as a third hand to help support baby in position while you work on achieving a latch. Many people manage to feed happily and safely in slings, once they are armed with good information, and know what to watch out for. It usually works best with older children, too. If you feel unsure about feeding your child in your carrier, do get in touch with a professional who can give you some one-to-one help and advice.

A hip carry may work well (with a wrap/ring sling/cross strap buckle carrier/meh dai).


3) How can you make feeding in a sling as easy as possible?
For breastfeeding, think about ensuring easy access for your baby. Your choice of clothes can make things a lot easier. Loose fronted tops that can be easily moved out of the way, pulled down or lifted up, or those that open and close with zips or poppers, rather than buttons can help. Many mums swear by a combination of a loose shirt that can be lifted up/pulled down with a stretchy camisole or vest underneath that can be lifted up/pulled down. Such layering often provides good cover, if required. Bras that are easy to undo one handed (while your other hand supports baby”s head) are also helpful. Some mums find latching on more successful if they lean forwards slightly to bring the breast up to baby’s mouth, and many need to hold their breast up with one hand for the duration of the feed. Hoods can help with providing some discreet coverage, but remember that temperatures inside slings rise quickly if air cannot circulate freely, and carbon dioxide levels in rebreathed air are raised.
4) What kind of slings are good for breastfeeding in?
It is usually possible to feed a baby in most slings, with a bit of care. I don’t think there is really any such thing as hands-free feeding, as one hand or arm should always be on your baby to provide support, especially before they have excellent head control. But one hand free is better than none! Breast size, shape, flexibiliity and nipple position varies from woman to woman, and from stage to stage in the breastfeeding journey, so each dyad will need practice to work out which height works best for them. Larger breasts may prove more tricky for some.
Please remember that baby’s back and occiput should be well supported with no curling over and his chin should not be resting on his own chest, and once finished feeding, baby will need to be returned to his previous snug, upright and close position, by adjusting the sling appropriately.
Feeding in Stretchy Wraps
There are many different ways to feed in a stretchy wrap. Some methods are safer than others. On the whole, stretchy wraps are mostly used with small babies in the classic upright “hug hold” also known as the “pocket wrap cross carry”. It is these young babies from birth to four months who have the greatest risk of airway obstruction, so it is worth visiting your local babywearing consultant to get some advice and support if you can. I can’t stress enough how important it is to ensure your baby’s back and head is well supported, but still able to move freely to create an effective latch (and delatch), and that baby’s face is visible, not covered with fabric and their nose is clear. Once the feed is over, baby MUST be returned to the previous snug, close, upright seated squat position. There should NEVER be any fabric behind the back of baby’s head.
The video shows how to use a stretchy as a breastfeeding aid. You can see how baby is in the classic tummy to mummy position as the fabric is removed.
I usually advise parents to see their stretchy wrap as a breastfeeding aid. It can add a layer of extra support and spread some of the weight to the non cradling shoulder, and allow a short period of moving around while their child is feeding. It is not hands-free.
Feeding in ring slings
Ring Slings and upright feeding
From a good seated squat position, the pouch can be gently and slowly loosened by lifting the uppermost ring up carefully, so that baby is lowered slightly down your body. Ensure that the loosening is equal across the width of the sling so that baby’s upright seated squat position is maintained. Bring your child to the breast up so he is able to latch on without twisting his neck.
- Bottle feeders may not need to lower their baby as much, but some loosening will help to ensure baby does not have to twist his head to the side too much for teat access.
.

Ring Slings and slightly reclined feeding
From the snug seated squat position, loosen the fabric slowly and carefully to lower baby just a little. Lean forwards slightly and support baby’s upper body with one hand. Gently recline your baby into the waiting crook of your arm as you bring his far leg around to your front so both legs are together. Ensure the pouch of fabric is well tucked up between your baby’s side and your tummy so he is resting as if in a hammock, slightly turned towards you, bent knees above bottom, feet outside the carrier, with his head and neck resting on your arm. Adjust his location in this position so his mouth is able to reach your nipple – it should look and feel just as if you were holding him in your arms to feed. Keep the top rail of fabric under baby’s neck, do not pull it over his head.
- Bottle feeding is similar, but baby’s head will be facing the ceiling.
Feeding in Woven Wraps
Woven wraps and upright feeding
Carries such as the Front Wrap Cross Carry and its variants can be easily adjusted for feeding. The knot at the back (or side) can be loosened just a little, with the resulting small amount of slack worked equally and evenly back along the fabric so baby is sitting in a lower pouch with mouth above nipple, but still snug and supported, and in the spread squat position. The whole carry can be moved slightly across to one side or the other, and the baby can then be brought to to the breast. It is easy to switch sides.
Hip carries (especially those with slip knots) are easy to feed from one side.
Bottle feeding is similar, but baby may not need to be lowered quite as much, and may need a little more space at the top edge for the bottle to be accessible without baby’s head having to turn too far.
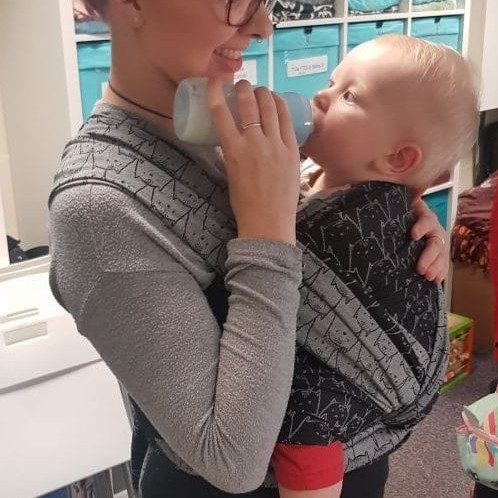

Woven Wraps and slightly reclined feeding
This works best with carries that do not have cross passes under baby’s legs, so baby can be gently tilted to one side to rest on your feeding arm. The FWCC can be partially untied so the long tails are hanging down over the shoulders and baby is sitting just in the horizontal pass. He can then be carefully gathered to one side with his far leg brought round to the front, his body turned to face the parent, bent knees above bottom, feet out and head and neck resting on your arm. Adjust his location in this position so his mouth is able to reach your nipple – it should look and feel just as if you were holding him in your arms to feed. Keep the top rail of fabric under baby’s neck, do not pull it over his head. The long tails are usually best left loose as retying them will mean you are not in control of baby’s head during the process.
- Bottle feeding is similar, but baby’s head will be facing the ceiling.
Feeding in soft structured carriers
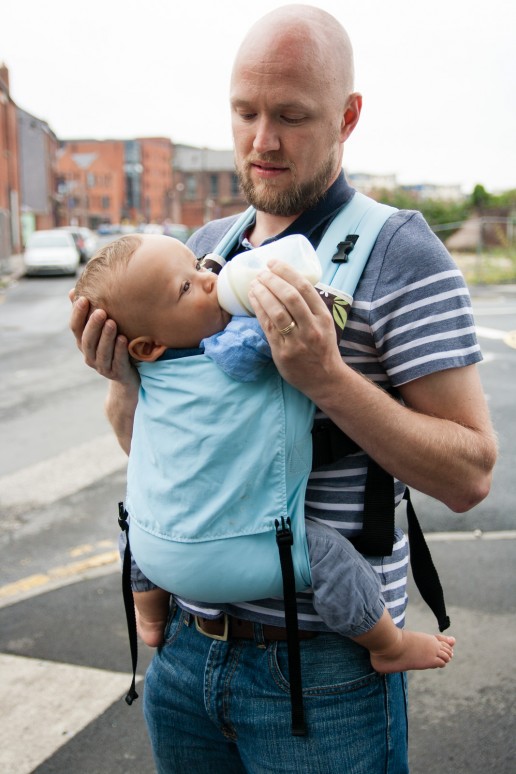
Soft structured carriers (mei tais, half buckles, full buckles) and upright feeding
This can work well for bigger babies who have some head control. Baby should be in the carrier at the height she would normally be carried, with back and legs comfy in the seated squat position. To feed, slightly loosen the waistband gently and lower it a couple of inches and retighten, then loosen the side buckles or ties one by one to lower baby to the required position. One side may need to be loosened more than the other as baby feeds from that side. The breast can then be brought to the mouth. It is usually easy to switch sides with the straps being adjusted each time to allow baby to move. Baby’s back and occiput should be well supported with no curling over and his chin should not be resting on his own chest.
- Bottle feeding is similar, but baby may not need to be lowered quite as much, and may need a little more space at the top edge for the bottle to be accessible without baby’s head having to turn too far.
Once finished feeding, baby will need to be returned to the previous snug, upright and close position, by adjusting the sling appropriately.



So in summary.. “Can I feed my child in my sling?” The answer is a resounding YES YOU CAN, from newborn to toddler, in lots of positions, from breast and from bottle. The key to doing it well is to ask questions about how to do it safely and empower yourself with knowledge to make a choice about how you wish to feed and then practice. It’s all about the AIRWAY! Do ask your local sling professional for some support…. – and enjoy!
Some further reading;
Seven Reasons Why Carrying is Great for Breastfeeding Mothers (Jess Hippey for Oscha Slings)

Carrying in the Postnatal Period
Is carrying in the postnatal period (in the early weeks after a baby is born) safe?
Babies want to be held close from the very moment they enter the outside world; they crave contact and many will spend their first few days and weeks sleeping in their parents’ arms and feeding frequently, enjoying this close interaction.
Pregnancy can be tiring and uncomfortable for many, due to our changing bodies and habits. We are no longer an upright species but a sedentary one, to our great anatomical and physiological disadvantages; chronic pain is a significant problem for increasing numbers of people in our society. Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction can be debilitating for pregnant women, and there is a growing belief that many women’s bodies are frequently not in the optimal condition to carry a child and thus take much longer to recover from pregnancy than our forebears. Ligament softening and laxity (from the hormonal changes preparing a body to deliver a fetus) can take some time to resolve fully especially if there has been pre-existing back pain and poor posture, and breastfeeding may prolong the effects of relaxin.
Labour, while exhilarating and empowering for some, can be exhausting for others, especially if prolonged. The recent historical practice of lying down for delivery is in marked contrast to how most women around the world across history and cultures have given birth (upright, squatting or kneeling). The natural birth movement and the emergence of doulas to support women with their delivery choices mirrors a growing desire to get back to our ancient human roots, which may also encourage speedier recovery from labour and birth.
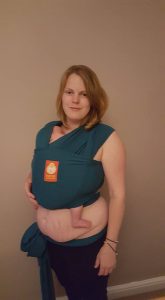
The rate of caesarean sections (both planned and as emergency) is high in Western society, currently between 20-25% of births in the UK (with some regional variation). A caesarean section is major abdominal surgery and some recovery time from this is to be expected, and varies enormously from woman to woman, depending on the reasons for the operation. Women are advised to avoid heavy lifting, “carry nothing heavier than your baby”, and not to drive for at least six weeks after birth. Scars can be uncomfortable and slow to heal for some, and some may experience abdominal pain for a while afterwards. Babies may come early and be very frail for several weeks.
Therefore it is not surprising that many mothers worry that after labour and birth, they may not be strong or well enough to carry their newborns in their arms for prolonged periods. Many will have toddlers at home needing the reassurance of their mother’s loving arms to help them cope with the newcomer’s arrival. Paternity or parental leave is often short; in a few weeks mothers are often required to manage at home alone.
Carrying your child in the postnatal period is important.
The early weeks are vital for bonding and attachment, providing continuity and security, promoting breastfeeding and helping to reduce depression. So yes, we should carry our babies somehow after birth. This doesn’t need a sling; people can hold their babies while sitting down and while reclining just as much as while they stand and walk around; it is the closeness and the contact and the skin to skin that promotes bonding and oxytocin release that matters. It helps to shape baby's brain, and also has a positive effect on yours! Furthermore it can be a great way to ensure any older children still feel connected to you, as your hands are free.
Carrying a newborn baby can be very healing if birth has been traumatic or there has been previous bereavement.
“"I had a tiny baby (4lb5oz) and experienced a traumatic birth, I suffered with PTSD. At times this meant I was very anxious and wanted to keep my baby close to me to be sure she was safe. I started with a stretchy wrap when P was just 3 weeks old. I truly believe babywearing strengthened my attachment with her and helped me to cope every day." Anon
There are some garments of clothing that can be worn in hospital or in the early weeks after birth; mimicking the practice of putting a tiny newborn down the front of the shirt. Some of these garments (known as skin to skin tops or kangaroo care clothing) are designed for keeping baby skin to skin to the parent while reclining, and are not hands-free.
Others are a little more structured (at least two layers of stretchy fabric) and provide enough support for baby that a parent can be hands-free and walk around, similar to a stretchy wrap. These can be most useful in hospital environments for their coolness and simplicity.
Please note that if your baby is premature or very small (under 6lb) it is wise to seek the advice of a specialist baby-carrying consultant; many "newborn" carriers, including some stretchy wraps will not provide enough support without guidance on how to use for these babies with special needs, and many buckle carriers will be much too big.
Breast and bottle-feeding can cause back, neck and shoulder pains, as can prolonged periods of one-sided carrying (which can also affect the pelvic floor and the symphysis pubis.) Being alert to the body’s signals of discomfort and acting on them to frequently redistribute the strain is of great benefit in building up tolerance and strength.
As women recover their strength and are able to do more each day, their mobile carrying abilities will grow too. As womens’ bodies settle back down after pregnancy, with appropriate pelvic floor toning and correction of posture and alignment, carrying will become easier. Furthermore, as baby gets bigger and heavier, the parent’s muscles will adapt to the gradually increasing weight and become more toned day by day, the more often they carry.
“Much of my pre-pregnancy life was spent in the mountains, and carrying my babies after their birth helped me get back in touch with my "home". It enabled me to very gradually and gently regain some fitness away from busy streets, and felt like less strain on the scar area than pushing a double buggy uphill.” Carissa

Keeping a baby’s weight high, snug and central will encourage loading across the large weight-bearing axes of the body, thereby preventing strain on muscles, ligaments and the pelvic floor, and avoiding abdominal pressure. Lifting a baby to the chest should be done carefully, with knees bent and upright posture maintained, and pelvic floor and core muscles engaged and active. Most types of carriers will be possible to use after a vaginal birth, and it will be a very individual and personal choice which. On the whole, most babies enjoy the gentle all-around pressure of carriers that can mould softly around them and be reminiscent of the uterine walls they have just left; and carriers that distribute weight widely across the parent’s upper body will be more comfortable.
If you have a sling that makes your back ache, please visit your local sling library or consultant for a fit check (often a few tweaks make all the difference) or to try an alternative. Cheaper carriers from supermarkets/Ebay often work much less well than better designed carriers and therefore last much longer. "My baby is too heavy for a sling" is usually an issue with the sling not fitting/not being well designed.
Carrying after a Caesarean

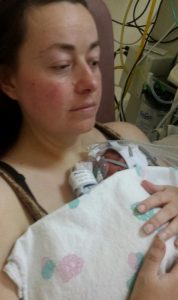
This is also very possible, and it could be argued, perhaps more important post section than after a normal non-instrumental vaginal delivery, depending on how the individual feels after the surgery. Achieving skin to skin as soon as possible is ideal, for promoting oxytocin release and bonding. This is vitally important after a section, especially if it was emergency and traumatic, thereby interrupting many of the biofeedback mechanisms around bonding. It is also important if the section was planned and baby was thus delivered before the biological hormone cascades of labour and birth were able to begin. There can be a strong tendency for women who did not have the birth experience they wished for to feel robbed and deprived of an important part of their baby’s arrival. The subsequent feelings of sadness and grief, or disappointment or that they have let themselves or their baby down somehow, however untrue, can significantly hamper the forming of attachment bonds and play a part in later postnatal depression or other mood disorders.
Mothers who experience this are very likely to find that skin to skin contact and frequent close touch and carrying extremely useful; the process of initiating and mantaining contact and loving touch often acts as a catalyst for the oxytocin release; this positive feedback mechanism will encourage loving feelings to develop despite the less than “perfect” start and get bonding well under way.
As soon as surgery is safely over and a well baby can be given to its mother, skin to skin can begin; resting on the mother’s chest under a blanket, inside a shirt or with kangaroo care clothing. Women are entitled to this skin to skin and should insist upon it; baby does not need to be washed or the cord to be cut before contact is achieved; the sooner the better.
Once mother is ready to move around and carry her child in her arms she can; she is advised to carry nothing heavier than her baby. Some women will choose to use slings immediately, if they feel ready (especially if they are already familiar with slings and feel confident with their use), others will wish to wait, especially if they feel unwell or are in pain. If the mother is confined to hospital and alone for parts of the day and wishes to move around, she may find the sling will help her to feel safer than carrying her baby loose in arms while she is still a little unsteady.
“Having a sling for carrying was very useful, as much easier and less painful than carrying in arms (less stress on abdominal muscles). It was great for bonding, especially since we were having trouble with breastfeeding.” Rebecca
The key factor is to avoid any carrier from irritating the wound or putting pressure on the abdomen. Double layer kangaroo-care shirts or other soft carriers such as stretchy or woven wraps, high-carrying waistband-less meh dais or buckle-tais and ring slings in frontal tummy to tummy carries, may be options to consider. Baby’s legs should ideally be tucked into the M shape, and this will also help to avoid feet kicking against a still tender wound. As the scar and any abdominal pain heals, carriers with more structured waistbands will become more accessible.
General tips about post-partum carrying (including fitness classes)

Participating in postnatal recovery programmes can be useful; however combining carrying and exercise/dance is usually best done with great caution as not every provider will have adequate knowledge about postnatal recovery (pelvic floor and diastasis recti issues) or about the rate and speed of each woman’s individual recovery from birth. Many may have no specialist knowledge about safe sling use or how to protect a baby from sudden shaking movements, as well as how to avoid overloading still-recovering tissues with certain stretching or weight-bearing activities with the extra load of a child in a sling. Walking with a baby in the sling, ensuring good alignment and posture, gradually increasing the speed and duration, is usually enough exercise for most women in the early months. Please do not rush; pelvic floor dysfunction is very very common (14 million women in the UK are known to have an issue, and many many more never seek help and remain undiagnosed). Leaking is NOT normal or to be expected. If you are unsure if your pelvic floor is recovering normally, please see your GP.
Read more about babywearing fitness classes here.
Using a sling allows families to settle back into the normal rhythms of daily life.
Often, older siblings are uncertain about the new addition to the family and uneasy about their place in it; they may need extra reassurance with the birth of a new baby. They may wish to return to their mother’s arms and be close to her body, for reassurance and reinforcing of the attachment bond.
Toddler carrying after birth
“During the intense post-birth bonding period with D I began to use a couple of wraps that had been favourites of R (the new big brother). It almost felt like a betrayal! But one afternoon, R asked if he could come up for a front carry in his favourite wrap, something he hadn't done for ages, and we twirled round the lounge together laughing while my husband cuddled the new baby. I think that was a really healing moment for us and let my eldest know he still had an important place in my arms too.’ Emma
However, toddler carrying after birth is much more of a challenge, especially if the pelvic floor is weak and there is diastasis recti (separation of the abdominal muscles from the stretching during pregnancy). Please seek help if your floor or core are weak.

Involving the whole family!
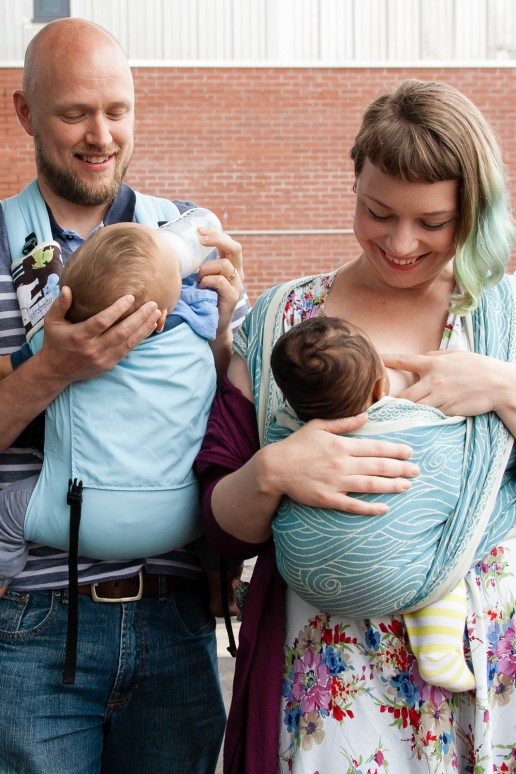
The post-partum period may be a great opportunity for other caregivers in the family to share the carrying and begin the bonding process. Whole families thrive when children are kept close; it spreads the load of child care around. Partners can carry their newborns, or their older children to provide reassurance.
“Carrying our eldest son (3) enabled my wife to give her attention to our new baby. It gave us much needed daddy and son bonding, at a time when he was feeling insecure with the arrival of the new baby.” Mal
Remember, it is the closeness and contact that matters; in arms carrying is as valuable as using a sling, and the shifting of your growing baby around your body as your muscles tire will help to rebuild your strength and endurance. Sharing the carrying with other members of your family will help to strengthen relationships and reduce the strain on your own body too.
Carry Me Daddy!
“Dear Daddy

When you hold me I feel happy. You are strong and I am safe in your arms. The more time I spend with you the more I trust you, and the more I can let you look after me when Mummy isn’t here.
I love to hear your breathing and the sound of your voice rolling around in your chest. I can hear your heart beating and it steadies me. I can hear you best when I am close to you. I love it when you look at me with your proud eyes, it makes me feel good. I feel loved.
I love being carried on your chest where we can chat till I am ready to snuggle contentedly to sleep.
I love my rides on your shoulders and on your back. The world is so interesting from up high!
I love the games we play and the way you make me laugh till I have no more breath in my body. I love it when you hold me on your lap to read to me. I love it when you hold my hand.
Carry me Daddy, while you still can!”
In-arms carrying and all other means of close and regular contact (such as noisy physical play) is of enormous value in building bonds between fathers and their children. 1 in 4 children lack strong attachment relationships, and slowly our society is recognising the need to address this. In arms carrying can be hard work, and a good comfortable baby or child carrier can make this much easier. Babywearing dads are becoming more and more visible, which is great news for families and for our society.
There can be a common myth that is only mothers who bond with their children in depth, and that the changes in her brain with parenthood are unique to her. This isn’t the case, fathers’ brains are also deeply affected by their caring role and they form strong, lifelong connections to their children if they are closely involved with their young baby as they grow. Bonding can be encouraged in many ways, not just though feeding the baby (which is another common myth). Babywearing is one tool for developing a deep relationship.
Here are some fathers talking about babywearing, what it means to them and why they do it!
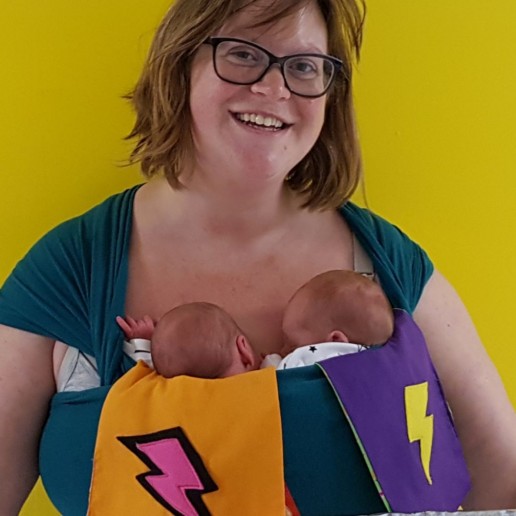
Mohamed
Babywearing! How are you faring? Are they still staring? As a father of twins who liked getting things done, there was only so far my two hands could take me when I had two babies to hold. I was hesitant at the science behind stretchy slings when I was first told you could carry more than 1 baby in them, the picture shows how quickly that evaporated into pure elation and joy. "I've got my hands back!" I remember thinking. That was the start to an awesome journey where there was nowhere I couldn't go with the twins. Beyond the physical strength which babywearing gave, I feel like it helped me show my girls that no matter what, I was able to lift them and raise them above whatever it was they were facing and give them a different view while still supporting myself. Why are you fearing if all you are doing is baby wearing?
Perinatal Mood Disorders and Carrying
The prevalence of Perinatal Mood Disorders (pre and post-natal depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder) is increasing in Western society as it is increasingly fractured and isolated, with a decreased sense of local community and shared care. The birth of a baby is often an overwhelming time for both parents, especially when also faced with the expectations and demands of a fast-paced culture that often judges people by their apparent productivity and appearance. As a GP, I see many families struggling with these conditions that are often diagnosed, and keeping babies close may play a part in surviving these illness, mainly due to the closeness with your child, rather than the choice of sling.
Postnatal depression is on the rise – affecting at least 10-15% of new mothers (with many more sufferers (and fathers) never being recognised to have the condition). Anxiety and PTSD are also worryingly common. Parents are encouraged to put their babies down as much as possible and regain their old lives; babies are expected to learn independence as quickly as possible and stop relying on their parents for their every need.
This approach to caring for children is very new in human history and runs counter to attachment theory, which suggests that the human infant thrives on responsive parenting and close contact.
Read about Ruth’s experience of antenatal depression here; for the rest of this post we will focus mainly on postnatal depression (PND).
What is Postnatal Depression?
Postnatal Depression is a depressive illness which affects between 10 to 15% of new mothers. Many more are never diagnosed with this condition, which can become a very significant issue in the functioning of a family. It is often poorly managed by health care providers, and can be misunderstood by the community and dismissed as “just the baby blues” or “tiredness.” It is common for sufferers to feel very alone and unable to explain just how they feel and why it is so difficult to endure. Prenatal depression is also experienced by many new parents, and postnatal anxiety and Post Traumatic Stress Disorder are also commonly experienced pre and postnatally.
Why is it so common?
Western society is increasingly fractured and isolated, with a decreased sense of local community and shared care. Depression is common in our culture, for reasons not clearly understood, but partly due to the way we live. The birth of a baby is often an overwhelming time for both parents, especially when also faced with the expectations and demands of a fast-paced culture that often judges people by their apparent productivity and appearance.
Before parenthood, people’s identities are often based on their roles and responsibilities in life; work, friendship circles, hobbies and interests. After a baby arrives, this often changes dramatically, sometimes in unexpected ways, and for many, the huge change in the pace of life and the loss of control can be very difficult to deal with. “The burden of conscious responsibility with no let up and the unusual and unexpected degree of fatigue can make a mother feel desperate about whether she can survive and how she will manage.” (Kennell & Klaus) This is the role that community used to play; supporting and carrying each other’s burdens as part of a committed and close-knit group of people who lived together, an experience that few parents enjoy in the West today.
What does it feel like?
Common words used to describe PND are guilt and inadequacy.
“The worst part was the guilt I felt about crying every day when I had a beautiful new daughter.”
“It isn’t about not loving your baby but about feeling overwhelmed with responsibility and unable to cope.”
“My head can feel empty and I have no thoughts.”
“It is just so hard to face another day of feeling totally unlike myself, missing my old life, unable to enjoy this new one.”
Fathers suffer from depression after birth too.
“The first few weeks were the hardest and I would just sit and cry. I felt like this shouldn’t happen to me, I should just be taking it on the chin and getting on with it. But the truth is, I felt alone and without the support of my wife, I would’ve been a lot worse.”
Many parents with PND feel a sense of dissociation and detachment from the child they want to love so much.
“It isn’t about not loving your baby but about feeling overwhelmed with responsibility and unable to cope.”
Caring for people with PND is hard.
“PND is the scariest and loneliest place on the planet and puts a terrible strain on the whole family.”
“My husband felt helpless because he knew something was wrong but I wouldn’t admit it and shut him out. All he could do was try to look after me and be there when I finally admitted it. It caused a lot of irrational arguments.”
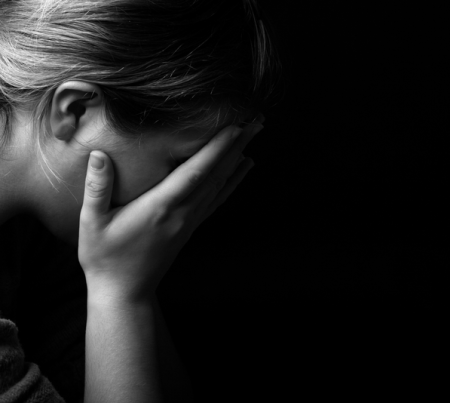


What can I do?
If you are suffering, or think you may be suffering from perinatal mood disorders, first be reassured that you are not alone and the vast majority of people with it survive with few long-term ill effects.
Here are some suggestions that may help.
Get help where you are.
Tell your nearest and dearest how you really feel.
“I found the hardest bit was to admit that I wasn’t coping, even when it looked like I was, I was fine on the outside but was a complete mess on the inside.”
Many women testify how supportive their partners and families and close friends are once they understand – ask them to help with the basic jobs of daily life; cooking, cleaning etc. Help them to see how useful you will find it when they listen to you with acceptance and without judgement, and how their understanding when things go wrong is vital. Guilt is a large part of PND and many kind people may inadvertently add to this burden.
Get help from your local health care providers.
This may be your GP, your midwife, your health visitor, your local SureStart centre. The quality of care from these resources can vary enormously. It can help to write down on paper how you feel in advance and what you think you need (validation, formal counselling, CBT or medication, for example) and take it with you to appointments. Continuity of care is great, if available; a HCP who listens and cares can make a greater difference than one who fires questions and is keen to tick boxes and prescribe medication at once.
“Guilt and lack of confidence are so typical of PND and my HCP was essentially validating those feelings even though objectively I was doing a great job!”
Be armed with information (e.g. if you wish to carry breastfeeding, sertraline is safe in these circumstances). The Breastfeeding Network is a valuable resource. If you are not satisfied with the care you are receiving, find different care.
Get help from your local non-NHS resources.
These can be very useful, such as HomeStart (a befriending service) and local PND groups. A postnatal doula may help, and there are many national helplines and resources (see below)
Get help from online social resources.
There are many forums and parenting groups full of people who know how you feel, and will listen and share. Being among people with the same values and parenting beliefs may be a source of great encouragement. Equally, avoid too much time online.
Get out!
It can be very hard to actually get out of the house when struggling with dark thoughts or hopelessness, but it is worth the effort involved. Even a walk down the road is a good start, and encourages release of endorphins (the natural feel-good hormone). Arrange to meet some friends, and ask them to encourage you to come. Try to make a plan for most days, and be kind to yourself if you decide on a pyjama day instead. Try to arrange some time to spend alone with your other half, to remember who you still are, as well as parents.
Get nourishment.
Good quality food, drink, exercise and sleep are vital to your own health and sanity, as are times to enjoy the things you used to. Dress well in bright mood-enhancing colours. You are still a person and your own needs should be met as much as your child’s. Some people make use of night-time carers to allow some much-needed uninterrupted sleep.
Get past your birth story.
For many women, recovering from birth takes a while, especially if it was not the hoped-for experience. The NHS Afterthoughts service and counselling can help if you feel a sense of grief.
Get a sling or carrier.
Keeping your baby physically close is well known to stimulate the release of oxytocin. Oxytocin is a hormone that is closely related to bonding and attachment. It is released during labour and breastfeeding, and, crucially, during skin-to-skin contact and social interaction. It has an important role in encouraging nurturing feelings and a sense of belonging, and reduces anxiety and depression by affecting cortisol release.
Babies who are in close contact with their parents have been shown to have a corresponding higher level of oxytocin than their non-carried counterparts; which subsequently helps to reduce baby’s own stress levels and improve their sense of secure attachment; their needs are met at the point of request. Calmer babies are easier to care for; win/win.
The soft touch of close skin to skin contact reduces the release of cortisol, the stress hormone, via C afferet fibres affecting receptors in the hypothalamic-pituitary-axis. Stroking has been shown to reduce pain responses.
Modern life is fast-paced and for many, constant carrying of ever-growing children can be difficult to achieve, or uncomfortable after the travails of birth. This is where the practice of using a sling, (sometimes known as babywearing) can be of great value. A soft sling that allows you to keep your child close to you, (thereby stimulating the release of oxytocin and reducing cortisol), and helps your baby to relax and sleep in secure comfort may make a huge difference to your life and your feelings and help you to feel that you can cope. Anxiety may settle a little as you know your little one is safe next to you.
“The sling brought us back to an almost pregnant-like state, with him a part of me, listening to one another’s cues. He was calmer for being close to me, which made me feel more confident, which brightened my mood. Leaving the house felt less daunting so I got more exercise and again increased my confidence. I talked to him more, whether he was awake or not, and he became my son rather than a tiny scary stranger.”
“My favourite thing in the whole world, that never fails to calm me or lift my mood has been cuddles with my baby, particularly skin-to-skin. For me, there is no antidepressant like it.”
“When she was in her pram I felt completely removed from her and her world. I was just an accessory, she was a job to do and I was irrelevant. Using a sling finally helped me bond properly with her and made a massive difference to the PND.”
Many slings are extremely comfortable to use, and can be very practical indeed. It is possible to learn how to feed discreetly in a sling, allowing you more flexibility about being out of the house for the day with your baby.
Slings give you and your baby the freedom to be on the move together, rather than feeling stuck; to go out into the world for a walk or go shopping without struggling with the complexities of a pram. Movement and exercise are vital to wellbeing; and using a sling safely can help your body recover from birth and become stronger.
Slings can be beautiful and colour therapy can help to lift the mood. Learning a new skill can be therapeutic, and many parents find a great sense of community among other sling users both locally and online. This can help with feelings of isolation, especially if you have chosen to parent differently from your family or your peers.



Get a sense of perspective.
What matters in these early months is you and your baby. It does not matter what other people think; the house does not need to be pristine, you do not need to impress people with how well you are taking to parenthood. I have heard many women describe how they “are falling apart on the inside”.
“I thought because I wasn’t suicidal or not looking after things that it couldn’t be PND so held back for a long time from accepting it and getting help.”
“I found the hardest bit was to admit that I wasn’t coping, even when it looked like I was, I looked fine on the outside but was a complete mess on the inside.”
Get confident again.
Reflect on what you have achieved so far and use that to build self-belief. Learn to trust yourself, be an instinctive parent – and you will fin that as you encourage others, you will find yourself lifted too. Some people find going back to work can be very helpful; the chance to use skills again and have adult interactions once more can be a great boost to self-confidence.
Useful Resources
Postnatal Depression Information Leaflet
Postnatal Depression Information Leaflet 2
Pre and Postnatal Depression Advice and Support (PANDAS)
Mothers for Mothers Postnatal Depression Support
Postnatal Illness Information (PNI)
The Impact of Babywearing on Mothers’ Mental Health – Aimee Gourlay
Further Reading
“I carry my heart in a sling” – a blog on how slings helped Lindsay fight her PND.
Sling Sally’s talk on Slings and Sanity for the 2015 Northern Sling Exhibition
Surviving PostNatal Depression – Selina Shaik for MIND
How Carrying Helped My Recovery – Ellie at Peekaboo Slings
Carrying With A Mental Health Disorder – Andrea’s story
Carrying Matters - all about babywearing safety, a guide to slings, and why connection matters
Welcome to the Carrying Matters website, run by the award-winning Dr Rosie Knowles.
It is important to support caregivers as they build a happy brain for their children. Soft touch and loving connections play a vital role in this. There are so many benefits of babywearing, which can be explored in this site. Babywearing safety matters; my guide to slings and my commitment to sling education will help parents and those who support them feel confident with sling use at every age.
Listen to Rosie talking about the 4th Trimester period in a new family’s life.
Search my website here
The positive effects of soft touch, close loving contact, and meaningful connections are enormous, and investment early on in family life is well worth it. Holding and carrying is connection; it matters to children, their carers, and society. The close contact helps to build a happy brain, and creates the relationships that buffer against adversity and promote resilience and long term positive health outcomes. It also helps mothers to survive the “4th Trimester” period and the months and years ahead. Here you can find everything you need to know about how to carry your baby safely and well, why babywearing is so normal and useful, how to choose a baby carrier, and help for all sorts of circumstances.
This page is run by Rosie Knowles, the author of the book Why Babywearing Matters (you can get a signed copy here). She is a GP in Sheffield, a carrying advocate and babywearing expert. She is passionate about supporting parents and carers to be close to their children; holding, soft touch and carrying matters in so many ways.
Recent Blog Posts
- Arms In or Out?
- Journeys to Recovery?
- Carrying a child with congenital heart disease, Abbie’s story
- Adversity and connectedness in the early months
- Parenting Criticism
- The importance of soft touch for infant development
- Babywearing in the time of Coronavirus
- “Babywearing for All”- helpful or harmful?
- Carrying with a weakened pelvic floor
- Babywearing and autistic caregivers

The simple act of connecting with a small person through the medium of loving touch has powerful and long-lasting effects on both child and carer. Babies need to be held close to encourage normal physiological and psychological development, especially in the early months. Every child needs love and connection to grow normally: the absence of responsive and supportive relationships that involve loving physical touch will hamper a child’s potential. Mothers heal best with their babies close to them.
Children thrive when they are carried, resilience builds and families flourish when the needs of all its members are met. Carrying is connection; carrying matters!

Keeping babies safe in any kind of baby sling or baby carrier is of paramount importance. The first most vital issue is to ensure that baby’s airway is open and unobstructed, with chin off the chest and the ribcage well supported. Babies’ temperatures should be considered too; they are surprisingly warm, and overheating can cause problems. Read more about sling safety here.

Secure attachment to other people is vital to human health and wellness; we thrive on relationship, on belonging. Such healthy attachments are the bedrock to future positive mental health and enjoyable relationships. However, 40% of children lack secure attachments, and are significantly disadvantaged. Encouraging carers to spend more time in close physical contact with their children is one way to improve children’s resilience and support everyone’s mental health. Soft touch is an essential part of building a happy brain and positive bonds that last a lifetime.
Read more about the importance of building secure attachments here, and how encouraging close physical contact can help build the resilience that children need to thrive despite adversity.

About Rosie
“I am a mum of 2, a family doctor in the UK (a GP), and a passionate advocate of building secure attachment relationships between children and their carers, due to the long lasting effects this has on future health. I believe that carrying children plays a large part in building such bonds, be it in arms or in a sling. With Carrying Matters, I focus on providing accessible information and education about this for parents and the professionals who support them. Sling and carrier use is not a new concept at all; but our Westernised society has lost the communal sharing of knowledge. We are no longer surrounded by a community of people who can help us get to grips with parenthood and share the load, so we need support in newer and more structured ways. This is what I do; empower people to keep their children close in a safe and positive way.”
Her book, “Why Babywearing Matters”, was published by Pinter and Martin in May 2016. It has been translated into several languages over recent years. She has written for a wide range of publications, including Juno Magazine, and has a regular freelance blogging role for Boba (links can be found in the Blog section).
She founded the Sling Pages, an independent website listing all the known sling professional resources in the UK and Eire, and the Building Bonds Project, a CIC supporting families in times of crisis and financial hardship to access good quality and safe carriers.
She is a practising GP in the UK with a particular interest in holistic medicine as well as children and women’s health and medical ethics. She began her career in hospital medicine but switched to general practice because of its flexibility with family life and the opportunities it presents to be more closely involved with communities, from cradle to grave. She has two children of her own, who have both been carried happily, and a husband who works alongside her at their local Sheffield premises. Rosie founded the Sheffield Sling Surgery and Library in 2013 and has supported thousands of parents across the South Yorkshire region, helped by a volunteer team of fantastic, committed parents who have found carrying their own children to be life-changing. They all want to help their fellow parents to discover this for themselves!
Rosie has won several awards for her work in this field; the Babywearing International Vijay Owens Babywearing Advocacy Award for Lifetime Achievement in Promoting Babywearing in 2016 and the 2019 Association for Infant Mental Health AIMH (UK) award in recognition of those who have highlighted and promoted infant mental health in their discipline.
Rosie developed the “Fourth Trimester” sling meet model with her colleague Lindsay Snow, focusing on the needs of parents with bumps to four months. Families often struggle to deal with the biological needs of their new baby within the confined structures and expectations of modern society, which can be damaging to the building of secure attachments.
The needs of baby and caregivers are both important, as is the mental health and happiness of the whole family. Human beings were not designed to live in small isolated units but in supportive social groupings.
Holding babies close (in arms or in a soft sling) can be a very useful tool for families struggling with mental health disorders, pre, peri or postnatally. The close contact and the soft touch has biochemical hormonal effects that can help to reduce anxiety, improve feelings of wellbeing and connection, as well as lifting the mood. Read more about this here.
You can find your local sling library or sling meet by searching the Sling Pages resource, get in touch with them!

Using a sling (carrier) helps parents to keep their child as close as their biology needs, while also being able to function as adults in a demanding and inflexible world.
Rosie trains carrying advocates and sling/carrier peer supporters and sling consultants, running courses in Sheffield and nearby. She has trained health care professionals, sling librarians, fitness course leaders and interested parents. See more here.
She lectures at conferences and gatherings around the UK and Europe about a range of topics, all related to early years parenting and how slings and carriers can make a huge difference to babies, their carers and to society.

“I’d highly recommend any enthusiast to attend this course. I found it thoroughly enjoyable and look forward to being able to use this new knowledge to help more parents discover the benefits of babywearing, as I have.”
“Rosie is a wonderful teacher, very clear and good at explaining. I felt she was well educated in her field and able to answer any question thrown at her. Also very friendly which made me feel comfortable and relaxed in a learning environment and confident to ask questions.”
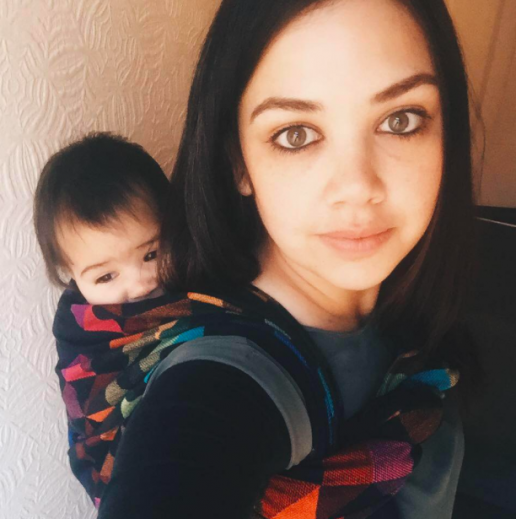



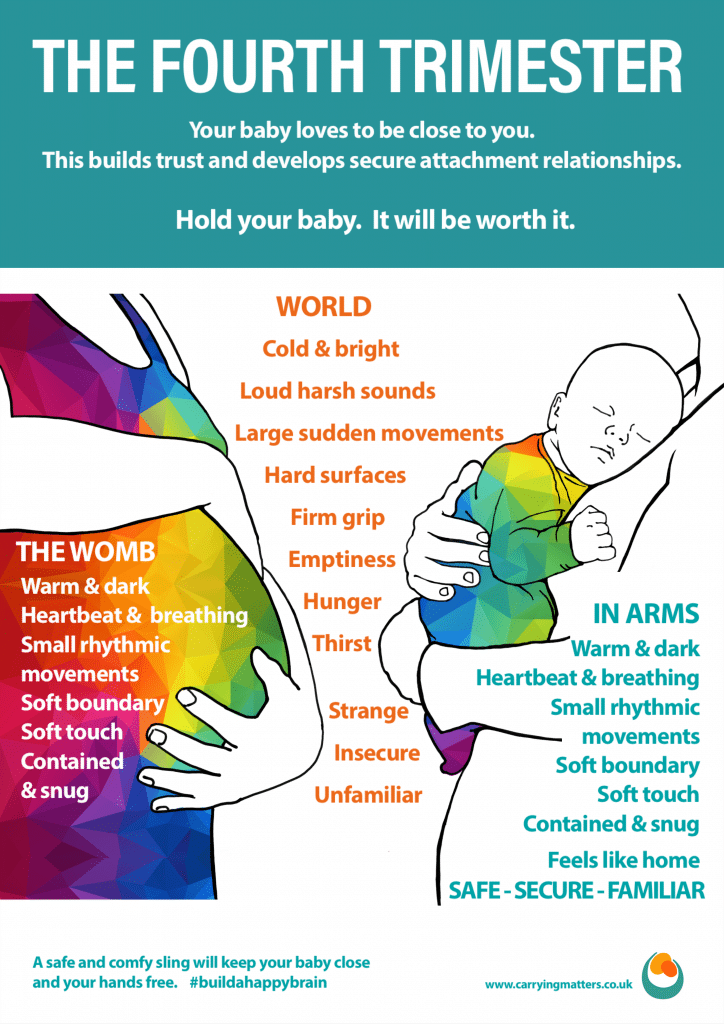




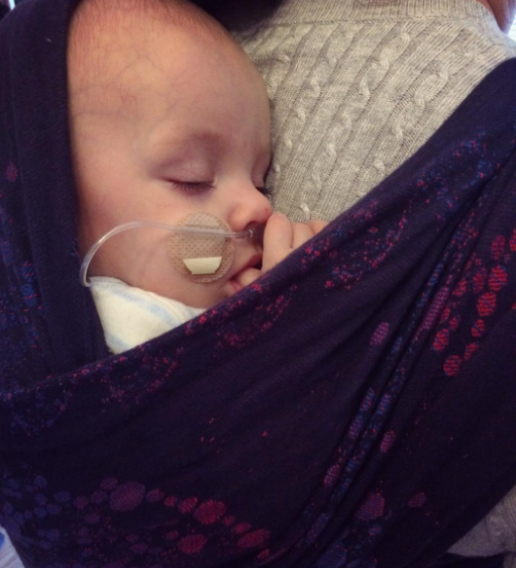
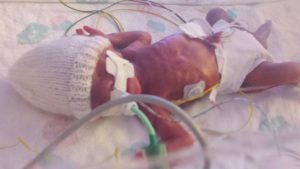
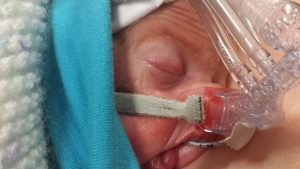


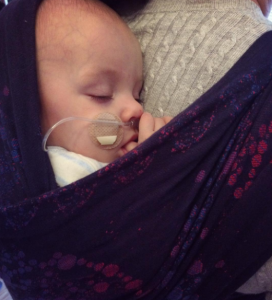









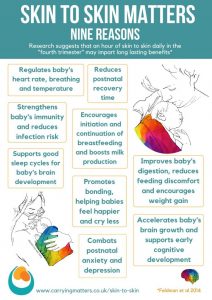 It reduces crying, both frequency and duration, (
It reduces crying, both frequency and duration, (